基本概念
传统JavaScript异步编程的形式大体分以下几种。
- 回调函数
- 事件监听
- 发布/订阅
- Promise 对象
异步
一个任务连续的执行就叫做同步。如果将任务为分两步执行,执行完第一步,转而执行其它任务,等做好了准备,再回过头执行第二步,这种不连续的执行就叫做异步。
回调函数
回调函数就是把第二步执行的任务单独写在一个函数里面,等到重新执行这个任务的时候,就直接调用这个函数。回调函数的英语叫callback,直译过来就是"重新调用"。
1 2 3 4
| loadData(url, function (data) { console.log(data); });
|
注意:任务第一步执行完后,所在的上下文环境就已经结束了,所以我们一般会使用var that = this 将第一步执行时的this 指向进行保存,以便回调时使用。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
| function Api(url) { this.url = url; this.request = function () { var that = this setTimeout(function () { console.log('url', that.url) }, 1000) } }
var api = new Api('http://127.0.0.1') api.request()
|
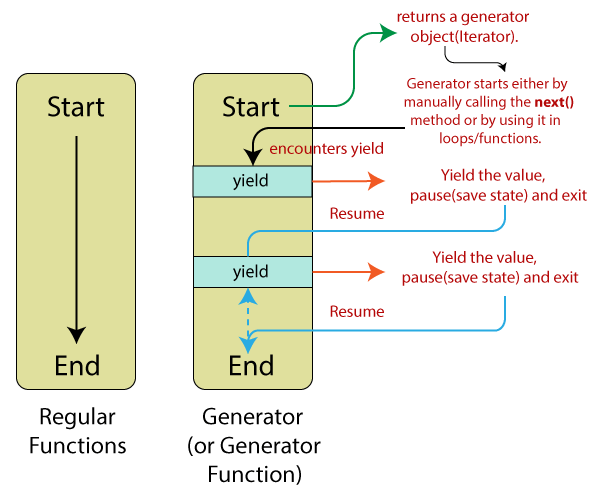
Generator函数
异步编程解决方案中, ES6还提供了Generator函数。它其实是一个普通函数,独有特征
function关键字与函数名之间有一个星号;- 函数体内部使用
yield表达式,定义不同的内部状态。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
| function* statusGenerator() { yield 'pending'; yield 'running'; return 'end'; }
var st = statusGenerator();
|
上面代码 statusGenerator 函数返回一个迭代器对象,函数内定义了三个状态,调用迭代器next方法指向下一个状态。
1 2 3 4
| st.next() st.next() st.next()
|
yield 表达式
yield表达式就是暂停标志。迭代器执行next时。
- 遇到
yield表达式,就暂停执行后面的操作,并将yield后面的那个表达式的值作为返回的对象的value属性值。
- 下一次调用
next方法时,再继续往下执行,直到遇到下一个yield表达式。
- 如果没有再遇到新的
yield表达式,就一直运行到函数结束,直到return语句为止,并将return语句后面的表达式的值,作为返回的对象的value属性值。
- 如果该函数没有
return语句,则返回的对象的value属性值为undefined。
for…of 循环
我们也可以使用 for...of进行遍历。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
| function* statusGenerator() { yield 'pending'; yield 'running'; return 'end'; }
var st = statusGenerator(); for(let v of st){ console.log(v) }
|
Generator 的应用
协程
**协程的意思是多个线程互相协作,完成异步任务。**它是一些编程语言的异步编程方案,比如go中的协程实现goroutine。协程序执行的大致流程如下:
- 协程
A开始执行。
- 协程
A执行到一半,进入暂停,执行权转移到协程B。
- (一段时间后)协程
B交还执行权。
- 协程
A恢复执行。
JavaScript中的协程实现Generator 函数,它可以在指定的地方(yield)交出函数的执行权(即暂停执行),然后等待执行权交还继续执行。
比如:我们实现一个倒计时函数,任务就绪后等待倒计时,一起执行。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24
| function* countdown(num, running) { do { yield num-- } while (num > 0) running() }
const tasks = [] const ct = countdown(3, function () { console.log('start run task') for (let task of tasks) { task() } })
for (let i = 0; i < 3; i++) { tasks.push(function () { console.log('task '+ i) }) ct.next() }
ct.next()
|
一个异步请求封装
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
| var fetch = require('node-fetch');
function* request(){ var url = 'xxxx'; var user = yield fetch(url); console.log(user); }
var req = request(); var result = req.next();
result.value.then(function(data){ return data.user }).then(function(user){ req.next(user); });
|
async函数
ES2017 引入了 async和await 关键字,使用这对关键字,可以用更简洁的方式写出基于Promise的异步行为,而无需刻意地链式调用promise。
async声明的函数一般称为async函数。可以把 async 看作是 Generator 的语法糖,因为它们本质的作用一样。
Generator 写法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
| const loadData = function (url) { return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) { resolve(data); }); };
const request = function* () { const user = yield loadData('https://user'); const goods = yield loadData('https://goods'); console.log(user, goods); };
|
async 写法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
| const loadData = function (url) { return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) { resolve(data); }); };
const request = async function () { const user = await loadData('https://user'); const goods = await loadData('https://goods'); console.log(user, goods); };
|
基本用法
async函数会返回一个 Promise 对象。当函数执行的时候,一旦遇到await就会先返回,等到异步操作完成,再接着执行函数体内后面的语句。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
| function timeout(ms) { return new Promise((resolve) => { setTimeout(resolve, ms); }); }
async function asyncPrint(value, ms) { await timeout(ms); console.log(value); }
asyncPrint('hello', 50);
|
async函数内部return语句返回的值,会成为then方法回调函数的参数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
| async function hello() { return 'hello'; }
hello().then(v => console.log(v))
|
async函数内部抛出错误,会导致返回的 Promise 对象变为reject状态。抛出的错误对象会被catch方法回调函数接收到。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
| async function hello() { throw new Error('Error'); }
hello().then( v => console.log(v), e => console.log( e) )
|
await 命令
一般情况下,await后面都是一个 Promise 对象,返回该对象的结果。如果不是 Promise 对象,就直接返回对应的值。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
| async function hello() { return await 'hello' } hello().then(v => console.log(v))
async function hello() { return await Promise.resolve('hello'); } hello().then(v => console.log(v))
|
错误处理
如果await后面的异步操作出错,那么等同于async函数返回的 Promise 对象被reject。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
| async function hello() { await new Promise(function (resolve, reject) { throw new Error('error'); }); }
hello() .then(v => console.log(v)) .catch(e => console.log(e))
|
所以最好把 await命令放在try...catch代码块中。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
| async function hello() { try { await new Promise(function (resolve, reject) { throw new Error('error'); }); } catch(e) { console.log('err:', e) } return await('hello'); }
const h = hello(); h.then((v) => {console.log(v)})
|
小结
本文记录了JavaScript异步编程中的一些方式,Generator函数和 async和await 语法,欢迎留言交流。
