简介
双重检查锁定(也叫做双重检查锁定优化)是一种软件设计模式。
它的作用是减少延迟初始化在多线程环境下获取锁的次数,尤其是单例模式下比较突出。
软件设计模式:解决常用问题的通用解决方案。编程中针对一些常见业务固有的模版。
延迟初始化:在编程中,将对象的创建,值计算或其他昂贵过程延迟到第一次使用时进行。
单例模式:在一定范围内,只生成一个实例对象。
Java中的双重检查锁定
单例模式我们需保证实例只初始化一次。
下面例子在单线程环境奏效,多线程环境下会有线程安全问题(instance被初始化多次)。
private static Singleton instance;
public static Singleton getInstance() {
if (null == instance) {
instance = new Singleton();
}
return instance;
}
下面例子主要是性能问题。首先加锁操作开销很大,因为线程安全发生在对象初始化,而这里做了做了全局控制,造成浪费。
public synchronized static Singleton getInstance() {
if (null == instance) {
instance = new Singleton();
}
return instance;
}
为了控制线程安全又能保证性能,双重检查锁定模式出现。
public static Singleton getInstance() {
if (null == instance) {
synchronized (Singleton.class) {
if (null == instance) {
instance = new Singleton();
}
}
}
return instance;
}
逻辑如下
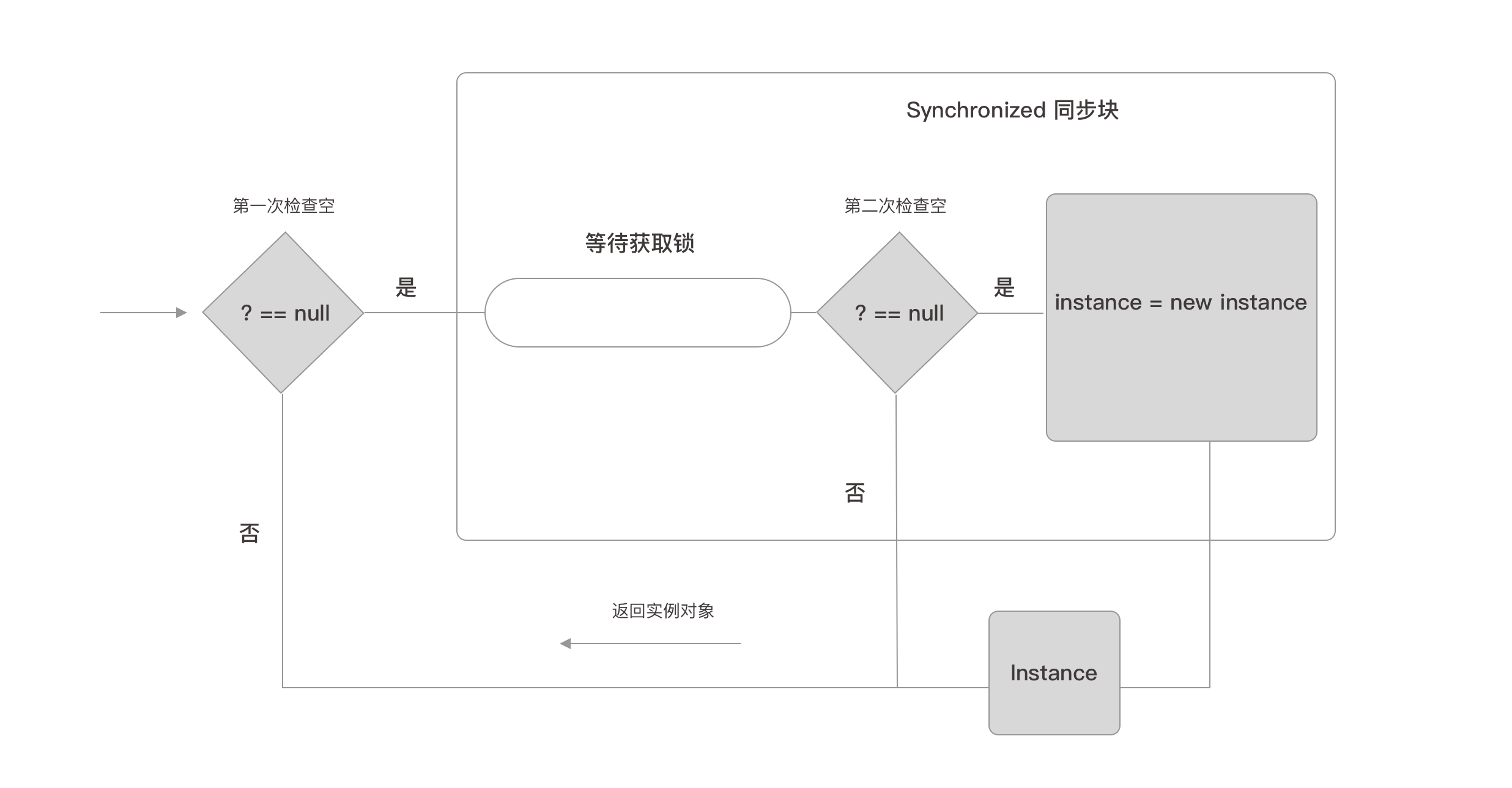
我们分析一下执行逻辑
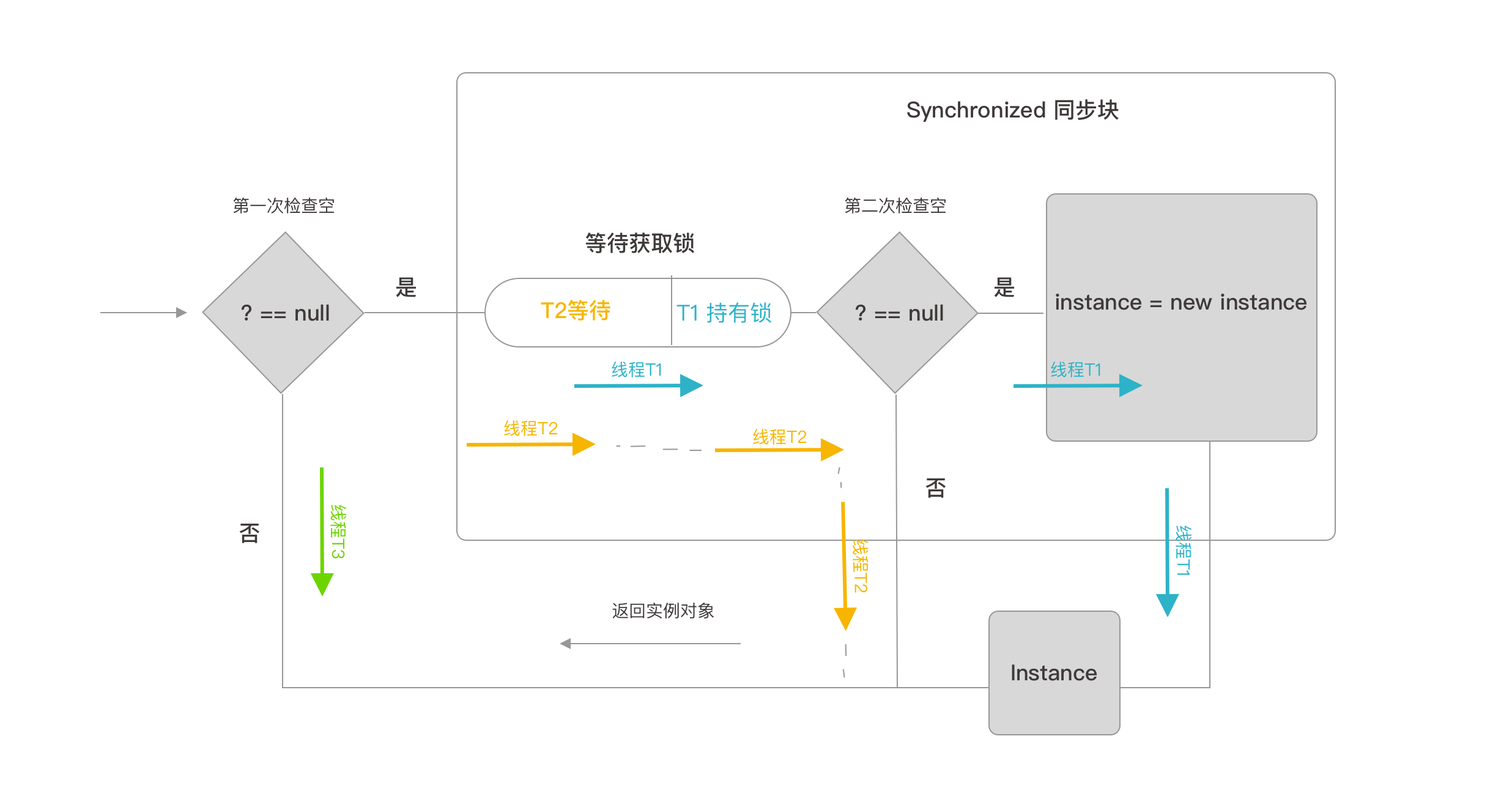
假设有三个线程 T1 T2 T3 ,依次访问 getInstance 方法。
- T1 第一次检查为Null 进入同步块,T1持有锁,第二次检查为Null 执行对象创建。
- T2 第一次检查为Null 进入同步块,T2等待T1释放锁,锁释放后,T2进入执行第二次检查不为Null,返回实例对象。
- T3 第一次检查不为Null,直接返回对象。
上面一切似乎很完美,但是这里面存在陷阱。根据Java内存模型我们知道,编译器优化处理会进行重排序。
instance = new Singleton() 大体分两个步骤;
1 创建初始化对象;
2 引用赋值。
而 1 2 步骤可能颠倒,会造成对象属性在初始化前调用的错误。
private static Singleton instance;
...
instance = new Singleton();
...
public class Singleton {
private int age;
public Singleton() {
this.age = 80;
}
}
这种细微的错误不容易出现,但是它的确存在。大家可以参考下面这份报告,里面详细记录这个问题。

http://www.cs.umd.edu/~pugh/java/memoryModel/DoubleCheckedLocking.html
报告里面也列举了几种解决方案。
1 利用 ThreadLocal
private static final ThreadLocal<Singleton> threadInstance = new ThreadLocal<>();
public static Singleton getInstance() {
if (null == threadInstance.get()) {
createInstance();
}
return instance;
}
private static void createInstance() {
synchronized (Singleton.class) {
if (instance == null)
instance = new Singleton();
}
threadInstance.set(instance);
}
2 利用volatile(解决重排序问题)
private volatile static Singleton instance;
public static Singleton getInstance() {
if (null == instance) {
synchronized (Singleton.class) {
if (null == instance) {
instance = new Singleton();
}
}
}
return instance;
}
下面是不同方案下的性能比较报告
http://www.cs.umd.edu/~pugh/java/memoryModel/DCL-performance.html
总结
本章节主要记录了双重检查锁定模式使用中应该注意的细微事项。
欢迎大家留言交流,一起学习分享!!!
